Anatomy of the Prostate Gland
Facts about the prostate gland
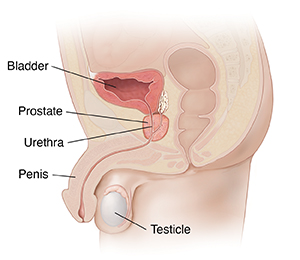
The prostate gland is about the size of a walnut. It's located just below the bladder, and it surrounds the urethra. This is a tube that carries urine and semen out of the body. The prostate is partly muscular and partly glandular. It has tubes (ducts) that open into the prostatic part of the urethra. It's made up of 3 lobes: a middle lobe, left lobe, and right lobe.
Function of the prostate gland
As part of the male reproductive system, the prostate gland’s main job is to secrete a slightly alkaline fluid that forms part of the seminal fluid. This is the fluid that carries sperm. During an orgasm, the muscular glands of the prostate help to propel the prostate fluid, and sperm that was made in the testicles, into the urethra. The semen then leaves the body out of the tip of the penis during ejaculation.
Online Medical Reviewer:
Marc Greenstein MD
Online Medical Reviewer:
Raymond Kent Turley BSN MSN RN
Online Medical Reviewer:
Rita Sather RN
Date Last Reviewed:
1/1/2023
© 2000-2025 The StayWell Company, LLC. All rights reserved. This information is not intended as a substitute for professional medical care. Always follow your healthcare professional's instructions.